UCLA Researchers Identify Molecular Program for Brain Repair Following Stroke
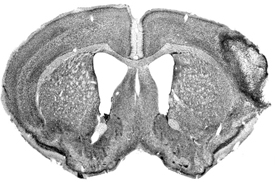
Mouse Stroke. An MRI of a mouse brain after stroke. The mouse section has been stained to show cell bodies. Image credit: University of California
A stroke wreaks havoc in the brain, destroying its cells and the connections between them. Depending on its severity and location, a stroke can impact someone’s life forever, affecting motor activity, speech, memories, and more.
The brain makes an attempt to rally by itself, sprouting a few new connections, called axons, that reconnect some areas of the brain. But the process is weak, and the older the brain, the poorer the repair. Still, understanding the cascade of molecular events that drive even this weak attempt could lead to developing drugs to boost and accelerate this healing process.
Now researchers at UCLA have achieved a promising first step. Reporting in the current online edition of the journal Nature Neuroscience, senior author Dr. S. Thomas Carmichael, a UCLA associate professor of neurology, and colleagues have, for the first time, identified in the mouse the molecular cascade that drives the process of reconnection or sprouting in the adult brain after stroke. (more…)

