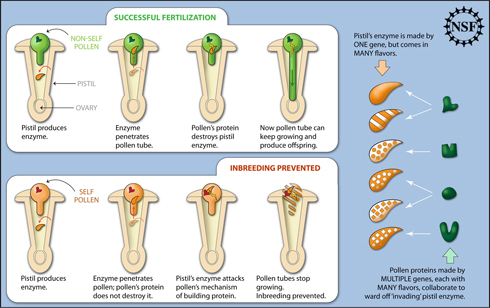
Plant Scientists Find Mechanism That Gives Plants ‘Balance’
EAST LANSING, Mich. — When a plant goes into defense mode in order to protect itself against harsh weather or disease, that’s good for the plant, but bad for the farmer growing the plant. Bad because when a plant acts to defend itself, it turns off its growth mechanism.
But now researchers at Michigan State University, as part of an international collaboration, have figured out how plants can make the “decision” between growth and defense, a finding that could help them strike a balance – keep safe from harm while continuing to grow. (more…)