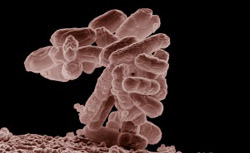
MSU Researchers Show How New Viruses Evolve, And in Some Cases, Become Deadly
EAST LANSING, Mich. — In the current issue of Science, researchers at Michigan State University demonstrate how a new virus evolves, which sheds light on how easy it can be for diseases to gain dangerous mutations.
The scientists showed for the first time how the virus called “Lambda” evolved to find a new way to attack host cells, an innovation that took four mutations to accomplish. This virus infects bacteria, in particular the common E. coli bacterium. Lambda isn’t dangerous to humans, but this research demonstrated how viruses evolve complex and potentially deadly new traits, said Justin Meyer, MSU graduate student, who co-authored the paper with Richard Lenski, MSU Hannah Distinguished Professor of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics. (more…)