Intricate, Curving 3D Nanostructures Created Using Capillary Action Forces
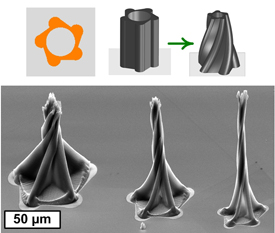
Twisting spires are one of the 3D shapes researchers at the University of Michigan were able to develop using a new manufacturing process. Image credit: A. John Hart
ANN ARBOR, Mich
.— Twisting spires, concentric rings, and gracefully bending petals are a few of the new three-dimensional shapes that University of Michigan engineers can make from carbon nanotubes using a new manufacturing process.
The process is called “capillary forming,” and it takes advantage of capillary action, the phenomenon at work when liquids seem to defy gravity and spontaneously travel up a drinking straw.
The new miniature shapes have the potential to harness the exceptional mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical properties of carbon nanotubes in a scalable fashion, said A. John Hart, an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and in the School of Art & Design.
The 3D nanotube structures could enable countless new materials and microdevices, including probes that can interface with individual cells, novel microfluidic devices, and lightweight materials for aircraft and spacecraft. (more…)
