Researchers Find ‘Goldilocks’ of DNA Self-Assembly
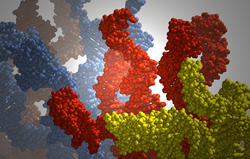
This image is a simulation snapshot of the molecular dynamics of DNA strands. Image credit: North Carolina State University
Researchers from North Carolina State University have found a way to optimize the development of DNA self-assembling materials, which hold promise for technologies ranging from drug delivery to molecular sensors. The key to the advance is the discovery of the “Goldilocks” length for DNA strands used in self-assembly – not too long, not too short, but just right.
DNA strands contain genetic coding that will form bonds with another strand that contains a unique sequence of complementary genes. By coating a material with a specific DNA layer, that material will then seek out and bond with its complementary counterpart. This concept, known as DNA-assisted self-assembly, creates significant opportunities in the biomedical and materials science fields, because it may allow the creation of self-assembling materials with a variety of applications.
But, while DNA self-assembly technology is not a new concept, it has historically faced some significant stumbling blocks. One of these obstacles has been that DNA segments that are too short often failed to self-assemble, while segments that are too long often led to the creation of deformed materials. This hurdle can lead to basic manufacturing problems, as well as significant changes in the properties of the material itself. (more…)
