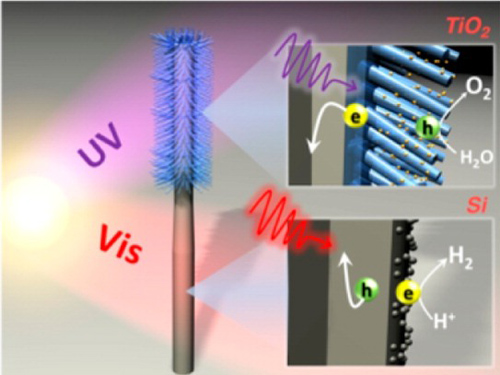
Schematic shows TiO2 nanowires (blue) grown on the upper half of a Si nanowire (gray) and the two absorbing different regions of the solar spectrum. Insets display photoexcited electron−hole pairs separated at the semiconductor-electrolyte interface to carry out water splitting with the help of co-catalysts (yellow and gray dots). Image credit: Berkeley Lab
(Visited 20 times, 1 visits today)
