Equipped with high-speed, high-resolution video, scientists have discovered important new information on how marine snail larvae swim, a key behavior that determines individual dispersal and ultimately, survival.
Researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and Stony Brook University grew Atlantic slipper limpet larvae, which are slightly larger than a grain of sand, and recorded microscopic video of them swimming. In previous studies, it has been commonly thought that larvae swim faster when they beat their hair-like cilia faster. However, this new microscopic video and research shows that this is not the case.
“I was actually quite surprised when I saw there was no relationship between cilia beat frequency and how fast they swim,” says Karen Chan, a WHOI postdoctoral scholar and the lead author on the study, which was published on December 18, 2013 in PLOS ONE.

Atlantic slipper limpets are common marine snails native to the northeastern coast of the U.S. (Photo by Karen Chan, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
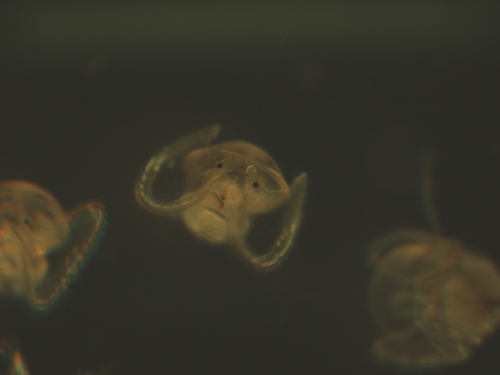
Microscopy image of Atlantic slipper limpet veliger larvae. (Microscopy image by Karen Chan, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
The larvae actually control how fast they swim by subtly shifting the position of their velar lobes – flat, disc-shaped wings fringed with cilia. The ability to make small movements with their velar lobes, akin to how a bird adjusts the angle of its wings while soaring, exhibits a more complex neuromuscular control than previously thought.
The Atlantic slipper limpet (Crepidula fornicata) is a common marine snail native to the northeastern U.S. It has become an invasive nuisance elsewhere in the world competing with endemic species, particularly in Europe. Co-author Dianna Padilla from Stony Brook University’s Department of Ecology and Evolution collected the abundant study species from the North Shore of Long Island, NY, for this research project.
“Collaborations between organismal biologists such as myself and oceanographers, who develop and use such clever technology, is helping us find answers to important questions that would otherwise be impossible,” Padilla says. She grew the larvae in her lab, which were sent to WHOI for video analysis.
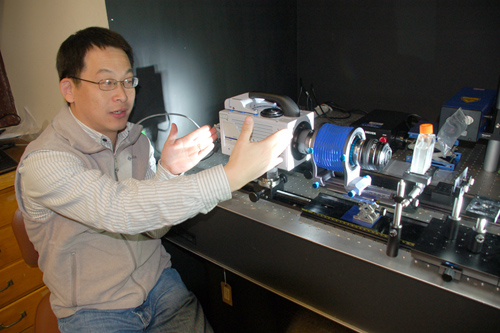
WHOI associate scientist Houshuo Jiang explains the system he developed that magnifies and records free-swimming microorganisms in high-speed, high-resolution video. (Photo by Alison Lee Satake, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
Houshuo Jiang, an associate scientist at WHOI and collaborator on this project, says their ultimate goal is to understand the limpet’s role in shaping the marine ecosystem and environment and climate in general.
With support from the National Science Foundation Biological Oceanography program, Jiang built a customized, vertically oriented optical system that can magnify and record high-speed, high-resolution video of microorganisms freely swimming in a vessel of seawater at 2,000 frames per second.
“Much more can be observed in great detail using this setup than observing under a microscope,” Jiang says.
Traditionally, scientists have recorded how fast larvae beat their cilia by placing a piece of transparency on a computer screen and tracing and counting the cilia by hand.
“We developed a method to do the same thing, but digitally,” Chan says.
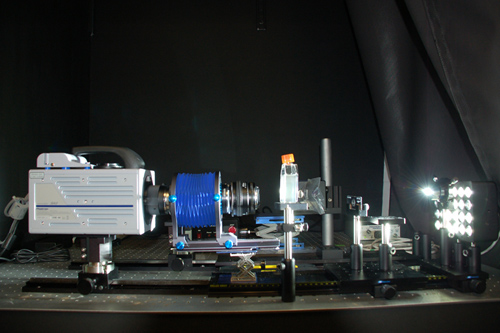
The vertical, optical system that magnifies and records freely swimming microorganisms, such as Atlantic slipper limpet larvae, developed by WHOI scientist Houshuo Jiang. (Photo by Alison Lee Satake, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
In the high-resolution video, the cilia alter from bright to dark as they beat up and down. Chan collected the bright to dark ratio and calculated for variation in order to time how fast and frequently a larva beat its cilia.
“This is a way to apply a new technique to address this old problem,” she says.
She also measured the length of each larva’s shell, the area of the velar lobes, and the distance between the center of the lobe and the center of the shell in order to calculate velar lobe orientation. She recorded and observed the swimming larvae from when they were two days old to 19 days old.
She found that within a single day, the larvae could vary their speed from swimming one body length per second to four body lengths per second.
“What this means is they have a lot of control over how fast they swim,” Chan says. And how they swim can determine where they may go.
“These results show the flexibility that these little animals have, which likely makes them so successful,” Padilla says.
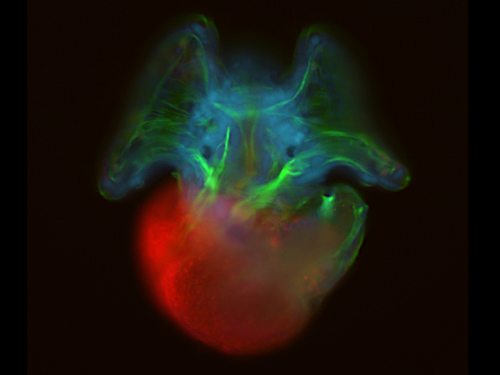
Epifluorescent microscopy image of an Atlantic slipper limpet (Crepidula fornicata) veliger larva. (Microscopy image by Andreas Hejnol, Sars International Centre for Marine Molecular Biology)

Atlantic slipper limpets have become invasive marine species around the world and are a nuisance especially in Europe. (Photo by Alison Lee Satake, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
Support for this project was provided by the National Science Foundation (NSF OCE-1129496 and NSF-IOS-0920032), the Croucher Foundation, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Coastal Ocean Institute and Ocean Life Institute.
*Source: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
